Search Engines – Getting Free and Paid Listings
[private_Member]

Click a link below for a specific topic
| # | Video | Length |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SEO | 17:08 |
| Website Magnets Sections: |
|---|
| 1. Search Engines – Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc (Organic & Paid) |
| 2. Social Media (Free & Paid) |
| 3. Directories (Free & Paid) |
| 4. Press Releases, PR & Articles |
| 5. Blogs (Yours & Post on Others) |
| 6. Posting Expert Comments on Forums |
| 7. Article Directories / eZine Directories |
| 8. Video and Blog Sharing Sites |
| 9. Articles on Partner Sites / Partner Newsletters |
| 10. Affiliates / JV Partners / TeleSummits and Alliances |
| 11. Emails / Email Newsletters |
| 12. Banner & Text Ads (PPC, etc) |
| 13. Webinars / Teleseminars |
| 14. Viral Marketing |
| 15. Tell-A-Friend |
| 16. Promotional Marketers (Groupon, etc) |
| 17. Offline Marketing (Networking / Out-reach, Public Speaking, Telemarketing, Direct Mail, Directories, Paid Ad Media, PR, Business Cards) |
Part 1: Search Engines – Getting Listed in the Free (also called Organic) Listings
Table of Contents
- 1 Part 1: Search Engines – Getting Listed in the Free (also called Organic) Listings
- 1.1 Paid Advertising on the Search Engines
- 1.2 SEO – Keyword Selection is Key
- 1.3 How to Get Listed in the Search Engines
- 1.4 Optimizing Web Pages to Rank High in the Search Engines
- 1.5 SEO Formula for Ranking High In the Search Engines
- 1.6 How to Find the Best Keywords for Your Web Page
- 1.7 How to Spy On Competing Websites
- 1.8 How to Select Your Ideal Keyword(s)
- 1.9 A Final Note About Optimizing Your Website
- 2 Part 2: Search Engines – Paid Advertising
 Search Engines are the Internet-based directories where people search for products, services and information. That’s why it’s so important (a) to be listed in the search engines and (b) to be listed high enough that you stand out from your competitors.
Search Engines are the Internet-based directories where people search for products, services and information. That’s why it’s so important (a) to be listed in the search engines and (b) to be listed high enough that you stand out from your competitors.
Although literally thousands of search engines are available, about 2/3rds of all Internet search engine use in the free world is with Google – with Microsoft/Bing and Yahoo each accounting for about 15%.
Therefore, the holy grail of online marketing is for your product or business to be listed high in the search rankings for these three (high on their first page when anyone types a phrase into their search box)
The best place to be listed is the search engine’s “organic” listings, but it’s also the most difficult place to show up. Organic are the natural listings a search engine presents when someone types a word or phrase (also called a keyword) into their search box. People using search engines tend to trust these “screened” listings more than the paid ads that generally appear above and to the side of the natural listings.
However, getting listed high in Google, Yahoo, Microsoft/Bing’s natural listings, particularly for competitive categories, can be tremendously difficult.
Paid Advertising on the Search Engines
Paid advertising is also available from the major search engines.
Paid advertising generally follows the “pay-per-click” model, where you pay a certain amount every time someone actually clicks on your ad.
The price you pay is based on an auction system, where you select a price based on what competitors are paying. Then, depending on the time of day and number of competitors at a specific time, you get charged at or below the price you set whenever someone clicks on your ad.
Prices typically range from 30 cents a click to more than $50 for the hyper-competitive categories like financial services.
SEO – Keyword Selection is Key
Regardless of whether you have organic or paid advertising, the most important element of any website and page on your website, is which keywords you are listed under for the search engines.
A keyword is a word or phrase people type into the search engine when looking for a product or business like yours. Every different word and phrase is a different keyword. “dog food” — “dog foods” – “food for dogs” and even the misspelling – “dogs foods” – each of these is a different keyword.
“Search engine optimization” (SEO) refers to the process of structuring your web pages so they rank high in the major search engines. This is done by meeting certain “rules” that have been set by these search engines. (examples of the rules are below).
Generally, every page on your website will be “optimized” for separate keywords, depending on the page’s content.
A pet food website may have a page for “dog food,” one for “cat food,” and one for “dog brushes.” Therefore, the ideal keywords for each page will be different, depending on a page’s subject matter.
Ideally, each page on your website will be “optimized” for 1-3 keywords. So a dog food page could use the keywords “dog food,” “healthy dog food,” and “all natural dog food” if that is relevant for what’s being offered on a specific page.
With so many potential word combinations (keywords) to choose for a specific page, people generally use a service to determine which keyword or keywords are best for a specific page.
The most commonly used of these tools is Google’s free Keyword Tool (described later in this section). The Keyword Tool shows you how many people have clicked on each keyword in the past month, and other information that may help you decide which keyword may be best for a specific page.
How to Get Listed in the Search Engines
Google and the other search engines continually sweep the Internet searching for new websites and web pages that have been posted. An easy way to tell if they have found your website or web page is to type your URL/web address (www.MyWebsite.com) into Google and see if it comes up.
Generally you do not need to submit your web address to Google and the others. They sweep the Internet so thoroughly that it is unlikely they will not find you.
However, although generally unnecessary, you could manually submit your website or web page to Google at http://www.google.com/submityourcontent/, to Microsoft/Bing at http://www.bing.com/toolbox/submit-site-url and to Yahoo at http://search.yahoo.com/info/submit.html. You’ll probably need an account (free) for each search engine you want to submit to. These sites each have a link to set one up.
Also, Google and the others will revisit your website periodically to check if you have added new content pages. They recognize that certain websites are continually posting new content, so they want to be sure to have important new content as it gets posted.
For this reason, Google and the others recognize that news websites, blogs and certain other types of websites post content more regularly than most others. If you have a blog or a WordPress website for example, there is a greater likelihood that Google and the others will visit your website more often than other websites, searching for new content.
Generally, once the search engines discover your website, their spiders (computer programs that scan your website looking for new content that may be valuable to others) will visit your website, then again soon after to determine if there is new content, then soon after again. If they find new content, your website will be put on a schedule to be visited often, to catch new content when it is posted. If not, the time between visits will stretch out, eventually to 60 days and perhaps longer between visits.
Optimizing Web Pages to Rank High in the Search Engines
To get your website listed high in the search engines, there are three factors they consider:
1. COMPETITION – How many competing pages exist;
2. RELEVANCE – Who is the content most relevant to; and
3. BACKLINKS FROM AUTHORITY SITES – Who believes your content is valuable?
COMPETITION <<
When you enter a keyword into Google, after you hit ENTER, directly below your keyword is a number. That’s the number of competing pages Google has logged into its system, for that keyword. For example, “insurance” has 2 billion competing pages. In fact, for most one-word keywords have a massive number of competing pages.
Why is this important?
If you are competing with tens and hundreds of millions of web pages, regardless of how great your page, product or content is, it’s unlikely you will rank anywhere near the first page of Google, where most people stay.
That’s why most successful Internet marketers use a long-tail keyword, which is basically a longer phrase. Where “insurance” will have a gazillion competing pages, “motorcycle insurance” will have fewer, and “motorcycle insurance in Malibu, California” will have even fewer.
Here’s a simple rule of thumb – for whether you’ll be able to get to Google’s first page.
If you are using a professional to optimize your website or web pages, when there are 3-5 million competing pages or less, generally they should be able to get you ranked on the first page of Google pretty quickly.
We’ve been able to get on Google’s first page for keywords with 20 million competing pages. But it’s less likely, so figuring 3-5 million competing pages is a good rule.
By the way, this might seem like a large number, but for Google, 3-5 million competing pages is not a very large number and you can often get ranked high pretty fast.
If you are doing it yourself, you should shoot for 300,000-500,000 competing web pages, where with a little work you can get ranked on Google’s first page.
That’s why, the long-tail keyword can be so important.
In Google’s Keyword Tool find keywords with plenty of people searching. Then click on that keyword in Google. If there are few competing pages (500,000 for you, 5 million for a pro), you will generally have a good shot at ranking on page one of the search.
RELEVANCE <<
Next is relevance. This means, do you have the keyword scattered throughout your content, but not overdone. If every sentence has your keyword, Google recognizes you are trying to fool them, and penalizes you for it, by giving your page a low ranking.
In general, your keyword should appear twice in the first three paragraphs, and then scattered throughout your content. Even YouTube videos must have keywords in the text, as Google (which owns YouTube) can actually read content within a video… and they do.
Your keyword should also appear in your headlines and elsewhere throughout the web page. (see a more complete list of the SEO rules below).
In any case, if your content (words, images, videos, etc) are relevant for a specific topic, you could rank well (to a degree) by the search engines.
One more important issue about keywords.
Certain keywords are more valuable than others. Particularly, the keywords people use when searching for information are not the same as those they use when they’re ready to actually buy something. These are called, “intent to buy” keywords, and they are extremely valuable to you.
For example, in trying to help an interior designer, we created pages optimized for the keyword “interior design” because Google’s Keyword Tool showed a ton of people searching on that keyword. We quickly discovered that most of those people had just seen a design show or read a design magazine, and were looking for free interior design tips.
We eventually figured out that people who were seriously searching for an interior designer would more likely use keywords like “interior design firms” and “interior designers in Malibu” than the more generic “interior design.”
So beware. When choosing the ideal keywords, make sure they are the ones someone with an “intent to buy” would use.
BACKLINKS FROM AUTHORITY WEBSITES <<
Last and most important – is getting backlinks from an authority website.
More than anything else you can do, getting backlinks from an authority website will get you listed right at the top of Google and other search engines.
Google has identified certain websites as authority websites. These include news sites like CNN, ABC News, etc., but also industry online magazines, local newspapers, and even many well-respected blog sites.
I know someone who got CNN, NBC and Fox News to interview him and post articles about his company on their websites. Because the articles included a link to his company’s website (a backlink), his website shot right to the top of Google, and has stayed there for years, even though he no longer even sells the product the networks talked about.
His website was not optimized, and he didn’t even choose keywords. He did nothing else to optimize his website. Nothing! The backlinks were enough to get him to the top of Google and keep him there, on pretty competitive categories.
So, how do you get backlinks from authority websites?
You’ll need to submit press releases through major press release services like PR Business Wire and PR Web, or contact major media directly – either national media like the news networks or publications in your industry.
BEWARE: Many offers are available online for people who claim they will provide backlinks for your website and web pages, but not only are they generally a waste of money, sometimes they will actually get you in trouble with Google.
Giant JC Penney is one of several companies that were punished by Google earlier this year because they tried to artificially boost their rankings, so be careful.
BACKLINKS FROM DMOZ AND YAHOO <<
Beyond conventional directories, there are two Internet-based authority directories that are highly respected by Google and the other major search engines. If you could get yourself listed and ranked high by these directories, you will generally be ranked high in Google and the others.
The catch is that it can be difficult, time consuming, and in the case of Yahoo, costly.
– DMOZ – this is part of the Open Directory Project, which is an international group of volunteers who are charged with building and policing many of the Internet’s key areas and functions.
The problem with them is, although getting a high rank from them could skyrocket your website to the top of Google and the others, because they are volunteers and geeks, it may take forever for them to get around to ranking your website or web pages. Still, if you do get ranked high by them, it could be highly valuable
To submit to DMOZ, go to: http://www.dmoz.org/ and click the SUGGEST URL link near the top. That will take you to the submission process.
– Yahoo Directory – this is a paid service from Yahoo where real people will review your website and rank it for the search engines. The cost at this posting is $299 for expedited service, and there is no guarantee they will rank you high. Still, if you have a quality product or service and a decent website, your rank should be positive.
To submit to Yahoo Directory, go to: http://dir.yahoo.com/ and click the SUGGEST A SITE link near the top right. That will take you to the submission process.
SEO Formula for Ranking High In the Search Engines
If you want to optimize any of the pages on your website so they rank high in the search engines, here are the key elements you’ll need to do.
(NOTE: You don’t need all of these, but the more you have the better):
>> KEYWORD – select 1-3 keywords for your web page. The fewer the better. Place that keyword throughout your web page in places the search engines look, such as:
– Content (scatter your keyword throughout your text, especially in the first two paragraphs, but not overdone. Maybe once in the first and once in the third paragraph (if you have short paragraphs. If you have really long paragraphs (not recommended) then have your keyword in two of your first three sentences). Your content should be 500-600 words. It could be more, but most search engines only read the first 500-600 words.);
Note: Search engines also like to see one or two synonyms of your keyword on your web page. For example, if your keyword is “dog food” you should have the words “pet foods” “dog food” “food for dogs” “natural foods” etc scattered throughout – maybe once or twice within your text.
A NOTE ABOUT WRITING CONTENT
It’s usually easier to write the text you want for your web page, then go back and add the keywords and synonyms after. This way your content will be interesting enough for your readers while also fitting Google’s rules.
– URL (put your keyword somewhere in your website or web page’s domain/ file name – www.KeywordHere.com/OrHereAlsoWorks — For example, if your keyword is “pet food” – your URL could be something like www.MikesPetFood.com or www.website.com/petfood)
– Title Tag (put your keyword in your web page’s TITLE tag and DESCRIPTION Tag. This is the first place the biggest search engines look so it had better be here.
– Headlines (put your keyword in some of the headlines on your page. Web page headlines are also called H1 (largest headline) and H2 (second largest headline) in the text formatting for your web page)
– Bold text (periodically bold a keyword that appears in your content – If my keyword is “dog food” I could have a phrase like <b> Not all dog food is good for your dog </b> made bold.)
– alt tags (these are the words that appear when your computer mouse scrolls over a photo, chart or graphic)
– Captions (which appear beneath photos, charts, captions)
>> EASY INTERNAL NAVIGATION (Google and the others like to see links to every section on most pages of your website, so a visitor (and their search spider) could easily get to just about any page or section on your website from any other page. That’s why many websites will have a directory at the bottom of their web pages)
>> LINK TEXT (when you have a link on your web page to another page, the search engines prefer when you use your keyword in the actual link – instead of having your link say “Click Here” – make sure your keyword is included in your link that people see, such as: “low fat dog food” or “Click here for low fat dog food.”)
>> BACKLINKS FROM AUTHORITY WEBSITES & SOCIAL MEDIA
– Getting backlinks from legitimate authority websites is one of the most powerful ways to get your website and web pages to the top of Google and the other major search engines. Do this by contacting them and asking them to write about your product or business; or by submitting a press release that will get your message to them. Always make sure you include a link to your website or web page in your bio that can be included in the article.
An authority website is the website from a major news organization (CNN, ABC, FOX, The New York Times, etc), local media (local TV and radio stations, newspapers, magazines), industry publications, popular blogs, and government and education websites. Whatever you can, get authority sites to post an article about you with a link back to your website, and this will go far to pushing you to the top of the major search engines.
– Backlinks from YouTube, Facebook and other SOCIAL MEDIA sites can also help your search engine rankings. If you have videos on YouTube (which is owned by Google), add a link in the video’s description to your web page. Also, put a link on your Facebook page to your web page.
How to Find the Best Keywords for Your Web Page
The simplest, most reliable, most commonly used source for keyword research is the free Google Keyword Planner (previously called the Google Keyword Tool). If you do not have a Google account or Gmail account, you’ll need to create one (it’s free – going through this process will prompt you to create a Google account).
Here’s how to find and use the Google Keyword Planner:
– In Google type “google keyword planner”
– Click the link that takes you to their site, then SIGN IN TO ADWORDS
– In the Keyword Planner, CLICK the top button –
SEARCH FOR NEW KEYWORD AND AD GROUP IDEAS
– In the top box (ENTER ONE OR MORE OF THE FOLLOWING), enter one or more descriptive words to describe your product or service – something that someone might type into Google to find your product or business (like “dog food” if that’s what you are searching for) –
NOTE: each one you type should be on a different line – when you hit ENTER it lets you enter the next one on a new line – For example, I could type “dog food” then hit enter and on the next line I could type “pet food,” and so forth.
– At the bottom of that page click the blue GET IDEAS button
– There are two tabs at the top of the list. Click the KEYWORD IDEAS tab
– This will give you a list of keywords related to what you entered, starting with the one(s) you entered
– On the right near the top there is a download button, which will let you put all the keyword ideas into an Excel spreadsheet
– Here’s what the top columns mean:
>>Average Monthly Searches – this is a count of how many people are clicking on that keyword every month. Start by selecting the ones with the highest numbers, usually thousands. You can click the Label of the column (AVERAGE MONTHLY SEARCHES) and it will sort them from highest to lowest)
>>Competition – this shows you how many people are paying for advertising on Google. Generally, if there’s lots of competition, that’s a good thing, because it means people consider it important enough to pay in order to have an ad appear whenever someone types that keyword into Google.
Remember – this only shows you who paid to advertise for that keyword. If you are paying for ads on Google, you may not want a “high competition” keyword because it means it will probably cost more because people are fighting (with their dollars) to be listed at or near the top.
However, when you are trying to find a keyword that you want your web page to be found on Google, etc, if there is a lot of competition and you could still get ranked high in organic search listings, that could be highly valuable.
Remember – once you find ideal keywords you’ll want to type each keyword into Google and look at the number that appears just below the keyword, for how many competing pages Google has found. Under 500,000 competing pages will generally give you a better chance of ranking high on the page, if you SEO optimize your website properly.
>>Suggested Bid – This shows you how much advertisers were willing to pay to be shown with this keyword. A higher price would only be interesting to you if it’s for a keyword you are interested in.
How to Spy On Competing Websites
The Google Keyword Planner also lets you enter the URL of competing websites so you can see what keywords they have selected. Here’s how…
>> Start by identifying some of the hottest keywords from your own research;
>> Type the keyword into Google and see which websites come up high on the page, especially on the natural listings (the non-paid ads);
>> Capture their website URL;
>> In the Google Keyword Planner, enter the competitor’s URL into the YOUR LANDING PAGE box;
>>Click the blue GET IDEAS button and it will show you which keywords this competitor has decided are most important.
How to Select Your Ideal Keyword(s)
Now that you have a list of relevant keywords, select your ideal keyword(s).
Here’s how:
>> DOWNLOAD the list
>> Select the keywords with the highest number of MONTHLY SEARCHES
>> Eliminate the keywords that don’t apply to you
>> Select the “intent-to-buy” keywords (the ones more likely for someone who isn’t just looking for information, but is probably ready to buy now)
>> Enter each remaining keyword into Google and see how many competing pages each has. The ones with 500,000 or less can be the best.
>> From here, create pages on your website that focus on the top keywords. Ideally, focus on one keyword per page.
A Final Note About Optimizing Your Website
Optimizing your website takes work, but it’s definitely something you can do.
If you hire an SEO expert, make sure it’s clear what you expect them to do, inspect which keywords they have selected for you, and then, make sure your page is ranking properly high for the keywords you want. Almost anyone could get you ranked high for a crappy keyword, but that’s not what you want.
Getting ranked properly could be worth thousands and more to your income and ultimate success online.
Part 2: Search Engines – Paid Advertising
Unlike free (organic) listings which generally take a lot of work and time to meet the rules of Google and the other major search engines, if you are willing to pay money, you could get listed high in the search engines for hot keywords almost immediately.
Like the free (organic) listings, you’ll first need to select the best keywords to be listed on (using the Google Keyword Planner).
You’ll also want to look at the COMPETITION column because that will generally indicate which keywords are the most expensive, where the most people are competing to be listed the highest on the page. The good news with paid advertising is you don’t necessarily have to be first on the page to get great results.
With some research using the process described in the SEARCH ENGINES FREE section, you can generally find great keywords to advertise on, particularly with long-tail keywords (with more words in the keyword – so rather than “insurance” you will choose “motorcycle insurance” or the longer phrase “motorcycle insurance rates” or even longer “motorcycle insurance rates los angeles” – where the longer phrase will have fewer competitors).
Search engine paid advertising uses the pay-per-click business model, where you pay only when someone actually clicks on your ad. The amount you pay is based on an auction, where they show you what competitors are paying and encourage you to beat them, or at least pay a certain minimum amount which will ensure that you are listed on the first page of the search results.
Prices per click generally range from 20 cents to $1.50 per click, but can be as high as $50 and more for highly competitive categories such as financial services.
Once you select the price you want to pay, that becomes a ceiling. You will never pay more per click for that keyword, but you may pay less, depending on the time of day your ad appears and the number of competitors for that time slot.
There is a daily limit that you establish, typically starting at about $4 per day. This is especially valuable because it means you won’t wake up to find you suddenly spent $1,000 or $10,000 on Internet advertising, and have no results to show for it.
As a new advertiser you will generally experiment to find the best ad that gets the most people clicking on it for the least money (easily adjusting the price and other factors, like which keywords you are showing up under… they make it easy to split test – where the search engines let you run two different ads at the same time and see which one gets better response). Systems like Google’s will generally provide pretty good metrics so you can see which keywords are best. They do this because they understand the more successful your advertising is, the more likely you will spend more.
You Don’t Just Want Clicks – You Want Conversions
Getting clicks is not enough. The real goal is to generate sales leads and/or make sales. You should spend a relatively small amount to generate a relatively large amount.
To do that, first you want to make sure you have selected “intent-to-buy” keywords, so only real buyers are clicking on your ads. Understand that many people are searching the Internet for information with no intent to buy, but some people are actually ready to buy, if they find a supplier they like and trust. These are the people you want, and they tend to type different keywords in the search engines.
For example, an interior designer discovered the keyword “interior design” mostly got people wanting free tips, maybe after watching a home makeover TV show or reading a magazine. By contrast, people “ready” to hire an interior designer were more likely to be using keywords like “interior design companies” and “interior design firms” indicating they were searching for which specific companies were available.
With products, people using the keyword “cameras” are more likely just investigating what’s available, but people typing “go-pro pricing” are probably ready to buy.
So understanding “intent-to-buy” keywords, the ones used by someone who’s ready to buy now, can be extremely important when it comes to selecting which pay-per-click keywords you want to be listed under.
Next, make sure your ad and the web page your ad links to say the same thing. Your ad doesn’t need to be linked to your home page. It can link to any page, including one you create just for this ad.
I see people create an ad that says one thing, then the person clicks on the link and end up at the home page, where the buyer gets confused.
If you’re paying for an ad, make sure, when the person clicks the link, it takes them to a page with the same or similar headline and text at the top. The landing page (the page the person lands on when they click the link) should be a continuation of the conversation you started with the small ad.
Content Network vs Google’s Network
Note that when you advertise with Google, they have two places you can advertise,
(1) their own Google Network – Google’s own website or websites that use Google’s search engine, and
(2) Google’s Content Network – which posts ads on other people’s websites, through the Google Adwords program (did you ever see the headline “Google Ads” on someone’s website?).
With their Adwords program, Google targets websites it believes will help you generate sales from your ads. This means you will sometimes even show up on a competitor’s website, which can be great… catching them before they buy from your competitor.
The bad news is, there can be cheating and false numbers from the Content Network (called click-fraud), where a hacker or competitor causes you to pay for extra clicks. Google has protections build-in that prevent multiple clicks from the same person to be counted more than once. And they effectively police their own site better than sites on their Content Network. Still, when you advertise on Google’s own site, there is less abuse and you are more likely to pay for real clicks.
Remember, Google wants you to be successful, so every way they can, they work hard to prevent click fraud and other abuses that could hurt your results.
Still, when you start advertising, particularly on Google, you should begin ONLY with Google’s Network and not use the Content Network (a simple check box).
Once your campaign gets rolling and you’re making great profit, you’ll probably want to expand to their Content Network, but usually at a considerably lower price.
Banner Ads Versus Text Ads
Most people starting with search engine advertising begin with text ads.
Google gives you computer code you can put on your web pages, to help you monitor which pages people click on and when they click on the BUY NOW page (it’s called “conversion”). This really helps you decide where to spend more or less money.
Once you find the ad and keywords that are converting best for you (making you money or generating actual leads), and especially once you start advertising using their Content Network, many people will start using banner ads, which can be more effective.
Banner ads are visual ads, usually with an image and/or text in a box. The image and/or text can be static or moving, although most banners have static images. The banner ad links to a page on your website which you select.
Banner ads with movement are created using animated GIF images, often with simple movement, or the more sophisticated Flash Animation, which can contain full-blown animation or even video (without sound).
Banner ad size is measured in pixels to accommodate for different computer screen resolution, magnifications and other factors. Free pixel rulers can be downloaded through www.cnet.com or are otherwise readily available online.

Sample Banner Ad (original web size 468 × 60 pixels, file size: 42 KB – enlarged for display here)
Banner ads can be vertical, horizontal or square of different lengths and widths, depending on the page that’s displaying it. Pages that allow banner ads specify which sizes are acceptable for display on their pages.
Many search engines include an easy-build section where you could make your own banner ads. However, getting them professionally made will generally provide more options and better graphics.
A simple search will uncover many professional banner ad creators available for hire, or lower cost ones can be found on sites like www.fiverr.com.
In each search engine’s ad section, they typically list the sizes they accept for banners in their network. For example, here are recent technical requirements for Google’s Display Network (always check the most current specs):
| Non-animated image ads | |
| File type |
|
| File size |
|
| Image size |
|
| Animated image ads | |
| File type |
|
| File size |
|
| Image size |
|
| Animation length and speed |
|
| Flash ads | |
| File type |
|
| File size |
|
| Image size |
|
| Animation length and speed |
|
| Flash version |
|
Keep in mind
Some image ad sizes are available only in some regions.
Here are more image ad sizes that you can use, depending on the region where you show your ad. These ad sizes are available for non-animated image ads, animated image ads, and Flash ads.
| Image ad sizes by region | |||
| Ad type | Dimension | Size limit | Regional use |
| PL billboard | 750×100 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Poland |
| PL double billboard | 750×200 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Poland |
| PL triple billboard | 750×300 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Poland |
| Vertical rectangle | 240×400 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Russia |
| Panorama | 980×120 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Sweden |
| Top banner | 930×180 | 150 KB | A popular ad size in Denmark |
| Triple widescreen | 250×360 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Sweden |
| Netboard | 580×400 | 150 KB | One of the more popular ad sizes in Norway |
Courtesy Google Adwords: https://support.google.com/adwordspolicy/answer/176108?hl=en
Here’s a chart showing the different sizes based on previous IAB recommendations (not actual size – displayed to show differences)
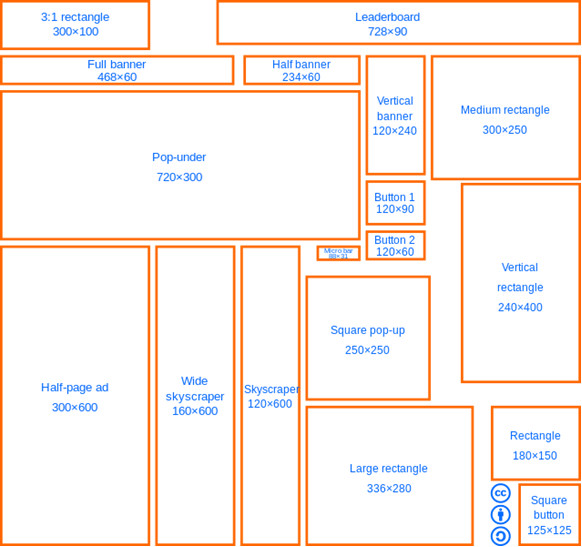
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Standard_web_banner_ad_sizes.svg
Important Rules for Search-Engine Pay-Per-Click Advertising
– Remember, you are paying for traffic
– The price of a click determined by bid auction
– Paid search position and ranking are based on the quality, relevance, and bid price of your ad. (If more people are clicking on your ads than others, Google will position you higher even if you didn’t pay for the higher position)
– Advertise on Google, Yahoo, and Bing/Microsoft…
– Also advertise on Facebook (which can be valuable because of the lower costs and better targeting), LinkedIn and other key sites
– Pay-Per-Click is harder than it looks, and can chew through your budget in the blink of an eye.
– For Google – the average click price is $0.30 to $0.80
– Highly competitive markets, like auto insurance and financial services can be as high as $30-$50 per click
– Monthly PPC budgets can easily reach $1,500/month ($50/day). Make sure you measure and achieve an ROI.
– Buy regionally and locally – you can also buy time of day, day of week
– Start low, 20 – 30 cents per click. It’s easy to change your prices quickly and/or stop a keyword or a campaign.
– Although most people start by choosing a single price for all their keywords (say 20 or 30 cents, then inching it up to make sure you are on page 1 of Google), you can actually pay different prices for different keywords – Google shows you what people are paying and what will get you (a) to page 1 and (b) to the top of page 1.
– Set your daily limit low. Remember $4/day x 30 days = $120/month.
– Raise your daily limit as revenues increase.
– Test, test, test. Make sure you are earning ROI from your ads.
– Use Google Analytics. Measure click through rate (conversion)
– Focus on “intent to buy” keywords.
– Separate Content Network from Google Network!!!
– Begin with Google Network – then pay half or less for
Content Network.
– Don’t always follow Google’s suggestion to spend more.
– #1 position is not always essential– but 1st page is.
– Track ROI of each keyword.
– Only a small percent of clicks buy – it’s about mass numbers.
– Google page rank is how they make sure buyers get what they really want. This means they look at the time people spend on your landing page they get to from your ad, and the relevance of what you are offering to the keyword.
ALSO SEE
.
If you’d like details about another Website Magnet — click on a link below
How will you bring “qualified” prospects to your website or web platform?
Search Engines | Social Media | Directories | Press Releases, PR & Articles | Blogs | Posting Expert Comments on Forums | Article Directories / eZine Directories | Video and Blog Sharing Sites | Articles on Partner Sites / Partner Newsletters | Affiliates / JV Partners / TeleSummits and Alliances | Emails / Email Newsletters | Banner & Text Ads | Webinars / Teleseminars | Viral Marketing | Tell-A-Friend | Promotional Marketers | Offline Marketing
[/private_Member]
